
lateral malLEOLAR FRACTURES
OVERVIEW: lateral malleolar fractures are fractures that occur in the distal aspect of the fibula. They can be distal, at or proximal to the joint line of the ankle.
CONSERVATIVE CARE: If non-displaced and stable, these fractures can be treated non-operatively with cast immobilization. Usually, 4-8 weeks nonweightbearing followed by protected weightbearing with a cast. Then a Cam Walker and physical therapy is initiated.
The x-ray image below is that of a non-displaced lateral malleolar fracture that will heal well without surgery (RED ARROW). The patient must be either immobolized and kept non-weightbearing in a cast depending on various factors including age of patient and pain level. Some patients do well with weightbearing protected immobilization in a cast boot. In a different patient, after conservative care, a patient with a healed high fibular fracture with fracture callus surrounding the fracture site is seen on the X ray (GREEN ARROW).


SURGICAL CARE: If unstable, and/or displaced, these fractures need to be brought to the OR to have open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). Usually, a plate and screws is utilized. Six to eight weeks of nonweightbearing cast followed by Cam Walker and physical therapy. Studies have shown a fibular fracture displaced by 1 mm can decrease the contact area of the ankle joint by 42%. If there is a small avulsion fracture off the tip of the fibula, these can often be treated by weightbearing cast immobilization followed by Cam Walker and physical therapy.
The x-rays below demonstrate a lateral malleolar fracture that is displaced and has shortening which requires surgical repair (left). Post-surgical repair with open reduction of the fracture with internal fixation involving screws and plate (right) allow re-alignment of the fracture fragments will allow the bones to heal correctly and in a timely fashion.

Pre and Post Operative X-Rays

Displaced filbular fracture with ankle dislocation. Fracture was repaired with plate and screws with a syndesomotic screw.

Pre and Postop Pics of ORIF Fibula Fracture with Deltoid Rupture

Pre and Post-op X-rays status post ORIF lateral malleolar Fracture (Below)

Pre and Postop X-rays of lateral malleolar Fracture
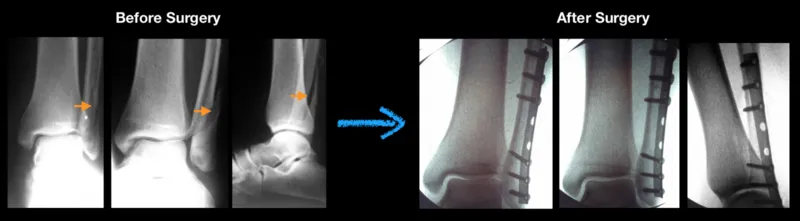
Series of Fibular Fracture

Series of 15 y/o Displaced Fibular Fracture with syndesmosis and deltoid rupture
Note displacement of fracture and increase space at medial ankle
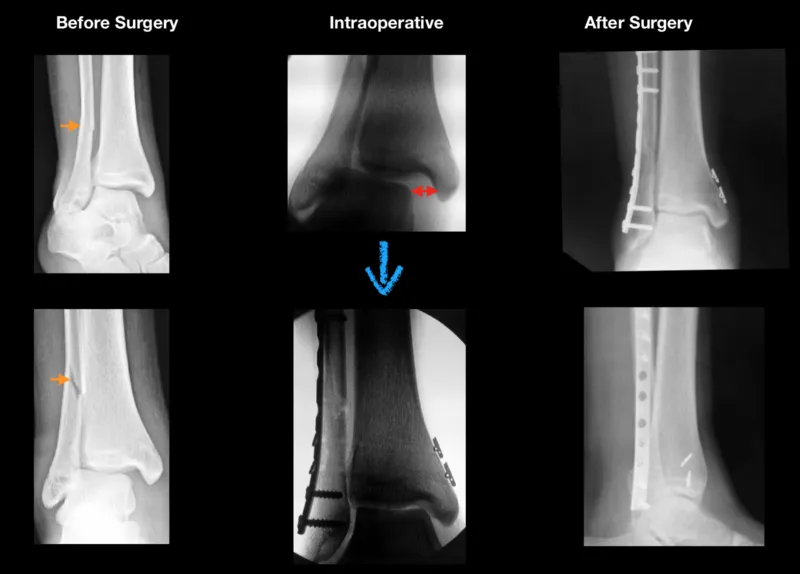
Intraop, stress of the ankle reveals even more widening of ankle joint (RED ARROWS)
Now, the ankle joint is anatomic and symmetrical. A plate and screws is placed on the fibula after reduction and 2 Arthrex Tightrope is placed across the syndesmosis to maintain reduction. This can be seen as the two "buttons" on the right side of the xrays on the tibia.
Pre and Postop Fibula Fracture ORIF (Below)
Plate and Screws are placed as well as a syndesmotic screw after reduction to give stability due to the ligamentous injury

After the deltoid and syndesomosis is healed, we replace the long screw (RED ARROW) with a Arthrex Tightrope (GREEN ARROW) that allows physiologic motion but maintains stability.
The button on the right of the bone is what holds the strong suture like material connected between the 2 bones.
Preop and Postop Fibula Fracture ORIF with Syndesmotic Rupture.

The circle shows the increased clear space which is abnormal and exemplifies a syndesmosis tear
The patient had a temporary screw (RED ARROWS) placed across the syndesmosis for 12-16 weeks and then permanently implanted an Arthrex Tightrope (GREEN ARROWS) to maintain stability but allow physiologic motion.
Fibula Fracture ORIF with Syndesmotic and Deltoid Rupture

The patient has an ORIF Fibula fracture and a temporary screw (RED ARROWS) placed across the syndesmosis for 12-16 weeks and then permanently implanted an Arthrex Tightrope (GREEN ARROWS) to maintain stability but allow physiologic motion.
Percutaneous FIxation of Displaced Fibula Fracture in Diabetic Patient









