ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
By: Robert H. Sheinberg, D.P.M., D.A.B.F.A.S.,F.A.C.F.A.S.
Impingements occur when soft tissue or bone is caught in the front part of the ankle when the ankle is in an up "dorsiflexed" position.
CAUSES:
- Repetitive movements (overuse) can cause swelling and scarring in the front part of the ankle without one single traumatic event.
- Ankle sprains can cause the ligaments and soft tissue to heal with scarring in the front part of the ankle causing an impingement more in the anterolateral aspect of the ankle.
- Chronic ligaments tears which cause instability cause compression of the medial talus over the medial ankle, causing an impingement that is anteromedial.
- Chronic repetitive stress over time can cause more bone spurs to develop in the tibia and/or talus, causing bony impingement.
- Ankle fractures are a common cause. Following an ankle fracture there is a large amount of swelling that develops in the joint. When the ankle is immobilized following a fracture (treated conservatively or surgically), scarring of the joint follows, causing an impingement or pain with movement of the ankle.
- Status post arthroscopy of the ankle residual scarring and/or recurrent scarring can cause pain in the front of the ankle. This can occur on the inner or outer ankle or both.
- High ankle sprains cause scarring of the ligament that connects the tibia to the fibula (anterior inferior tib-fib ligament). With the foot moving in the up position the main bone of the ankle (talus) moves up and gets abraded due to the thickening of the ligament as it is healed and scarred.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
- Stiffness or soreness is usually present in the morning when the patient rises. It may take a few minutes for the ankle to warm up and move more normally.
- After sitting for a long period of time and getting up, the stiffness can recur only again to loosen with normal walking.
- Tenderness is noted in the front part of the ankle whether on the inner or outer side with palpation.
- Trying to move the foot into the ankle will show a limited movement, especially when comparing it to the other ankle.
- Swelling is often seen over the area where a ligament or bone has been injured.
X-RAYS:
- X-rays are taken to rule out bony causes of impingement which include spurs off of the tibia, talus or rarely the fibula.
MRIs:
- MRis are often utilized when conservative treatment fails.
- We need to evaluate the soft tissue in the front part of the ankle and rule out an osteochondral defect of the talus or tibia (cartilage injury to the ankle bones)
TREATMENT:
- Conservative care includes rest, anti-inflammatories and physical therapy to lessen the swelling and scarring in the front part of the ankle.
- Steroid injections are performed if there is not an osteochondral defect. This helps to reduce the thickening of the soft tissue in the ankle joints.
- A short period of immobilization in a boot may be necessary to lessen the stress in the front part of the ankle.
If conservative treatment fails, then arthroscopic surgery is highly successful in removing the bony and/or soft tissue impingement that is causing pain in the ankle. The procedure is done on an outpatient basis under a twilight or general anesthetic. Within 18-24 hours the bandage is removed and the patient is instructed to move the ankle as much as possible to prevent scarring and swelling in the ankle that can cause a re-impingement to the area. Occasionally open surgery is necessary if the bony impingement is severe, restricting motion substantially to the joint. Still postoperatively early range of motion within 3-5 days is necessary to prevent scarring to the joint, which would preclude normal motion.
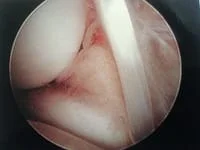
Impingement at the lateral aspect of the ankle joint with scar tissue on the intra-articular portion of the AITFL. This causes irritation in the joint with range of motion.
The impingement is at the upper right-hand corner. The instrument is shaving it down.
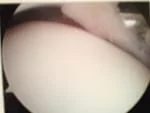
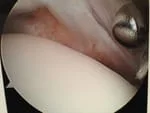

After removal of the impingement.


